[Tutorial] How to Revive E-Scooter Battery
We know how it sucks when you leave your e-scooter or e-bike in storage for sometime and it fails to turn on after you shake out the cobwebs.
Li ion batteries (in fact all batteries) have a natural discharge inherent in them. If they are connected to your electronic device (like an e-scooter) the natural discharge will be even faster even if you do not use the device.
What do you do now? That expensive e-scooter is essentially scrap metal without a working battery. You check with your scooter store and that replacement battery pack isn’t cheap. Good batteries are at least one third of the cost of the whole e-scooter.
There may be hope.
We can walk you through the process to revive that perfectly good battery. However, you have ensure that some preconditions are met before you proceed with trying to revive that battery.
Pre-conditions for Revival
- For a 36V battery pack, there should still be at least 20V remaining. For a 48V battery pack, there should still be at least 26V remaining. You can measure the voltage on the battery pack by using a multimeter like below.

- The battery pack has not been exposed to moisture and there is no evidence of water stains on the battery pack. You will have to open the battery pack and if there is water or moisture, it could cause a short which is what we want to avoid.
- Your battery pack is not bloated. Battery bloat means the battery cells within are damaged and should definitely be disposed off through the correct protocols.
- Your e-scooter or e-bike has been kept in a cool and sheltered place that isn’t above 40 deg C. So if it has been sitting in the back of your trunk and you just drove through the Australian outback, then we suggest to dispose the battery pack using the correct protocols.
Things you Need
The most important components in this delicate operation is:
- DC Power Supply
- A pair of jumper cables
- Pen Knife
- Heat Shrink Wrap
- Glue gun/silicone gun
- Flat head screwdriver

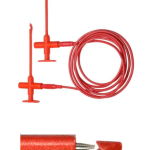



Steps to Repair your Battery
1. Opening up the Battery Pack
If you have a Li Ion battery soft pack like below, slit the packaging along the edges using a pen knife. Be extremely careful when doing this.
Remember not to cut too deep so that you do not accidentally puncture the battery cells inside. However, if you have a Li Po battery on the right hand side, DO NOT try to cut it open.


If you have a hard case battery which could come in many forms, you would have to use a screwdriver to remove any screws and a flat head screwdriver to pry open the casing. Sometimes, there would be a silicone seal. If so, you would have to cut that seal open with a pen knife.
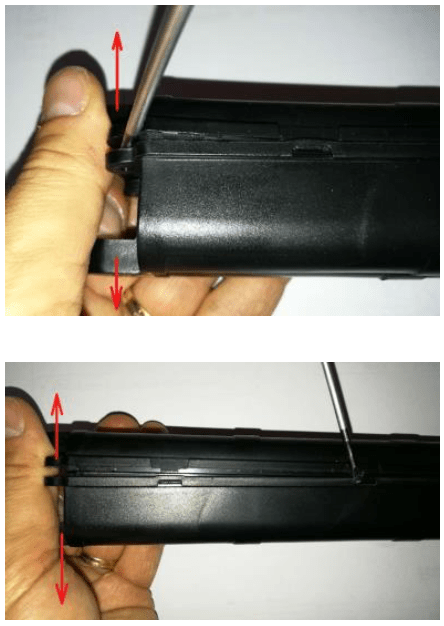
Use a flathead screwdriver to pry open the hard case

Opened hard case Li ion battery
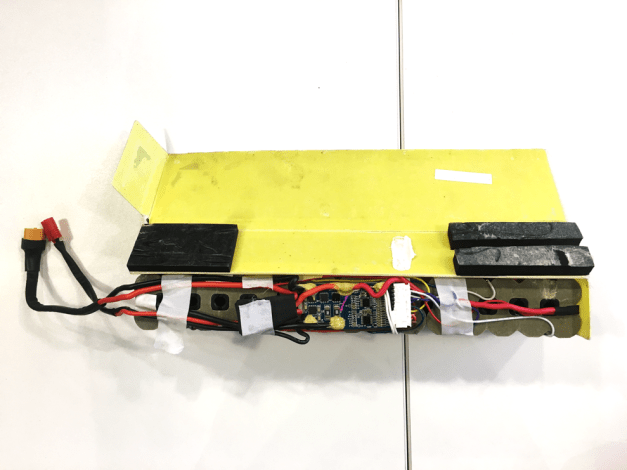
This is what an opened soft li ion battery pack looks like
2. Connect the Wires to the DC Power Supply
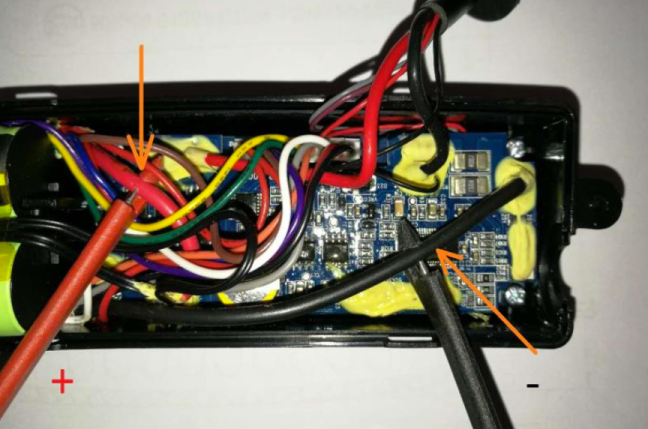
Once opened, you will see a PCB protection board like the one below. Look for the 2 main Black and Red wires as pointed out in the arrows below.
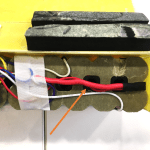
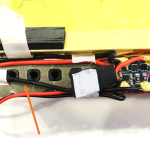
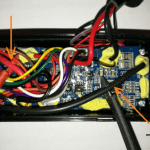
They are normally thicker than the other wires (as they are the main charging wires) and the black wire will typically be at one end and the red wire will be on the other end of the PCB.
On your DC Power Supply like below, set the following charging parameters: Voltage 30V and Current 0.15A

DC Power Supply settings for 36V battery
Connect the red and black wire probes from the DC Power Supply to the red and black wires (arrowed above).

Opened hard case Li ion battery
If you do not have the needle probes that we use in the pic above, then you will have to make a small incision on the red and black wires to connect the probes.
Once the probe is connected, and the DC Power Supply has started charging, you will see that the voltage will rise very quickly initially. However, the voltage rise will gradually slow down so do not be alarmed if it takes a much longer time for the voltage to rise.
Stop charging when any of these 3 conditions are met:
- Voltage reached 30V for a 36V battery pack and 39V for a 48V battery pack.
- Or when charging current has slowed down to 0A
- When voltage does not increase beyond a certain voltage level despite a long charging time. It means there is a dead battery cell which is a whole other topic of discussion altogether.
Remove the charging probes from the wires on the PCB. If you had made an incision in the black and red wires, use a glue gun to patch up the hole and insulate the wire.
3. Repacking the Battery Pack
For the hardcase battery pack, seal up the seams using either silicone or glue and press them back tightly. Replace any screws necessary.

Patching the battery casing
For soft battery packs, replace the old heat shrink wrap with a new one and use a hot gun or a hair dryer to shrink the wrap down to size. Once its tightly set, apply silicone to the seams of the shrink wrap like in the pic below.
battery pack with silicone seal
4. Charging Normally Using Charging Adaptor
Once the battery pack is sealed, use the original charger that came with the e-scooter or e-bike to charge the battery pack normally until it charges fully.
The full voltage for a 36V battery is 41V and full voltage for a 48V battery is 52V. Use a voltmeter/multimeter to test for the voltage once the charger has indicated a full charge.
So there you have it! You can save yourself a few hundred dollars by following these steps. If you are not confident of performing these steps yourself, get a professional e-scooter or e-bike workshop to do it for you.
